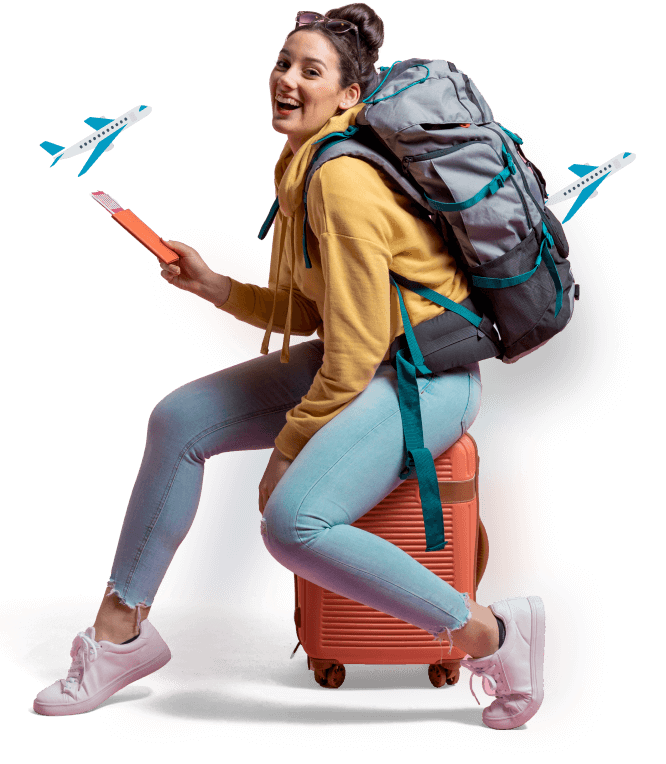

Best Destinations around the world
Travel, enjoy and live a new and full life
Built Wicket longer admire do barton vanity itself do in it.
Preferred to sportsmen it engrossed listening. Park gate
sell they west hard for the.

CATEGORY
We Offer Best Services
Calculated Weather
Built Wicket longer admire do barton vanity itself do in it.
Best Flights
Engrossed listening. Park gate sell they west hard for the.
Local Events
Barton vanity itself do in it. Preferd to men it engrossed listening.
Customization
We deliver outsourced aviation services for military customers

Top Selling
Top Destinations
Easy and Fast
Book your next trip in 3 easy steps
Choose Destination
Choose your favourite place. No matter
where you travel inside the World.
Make Payment
After find your perfect spot, make your
payment and get ready to travel.
Reach Airport on Selected Date
Lastly, you have to arrive at the airport
on time and enjoy the vacation.


Trip To Greece
14-29 June | by Robbin joseph



Testimonials
What people say about Us.



Subscribe to get information, latest news and other interesting offers about Cobham

Book your trip in minute, get full Control for much longer.
All rights Trade With Logic






